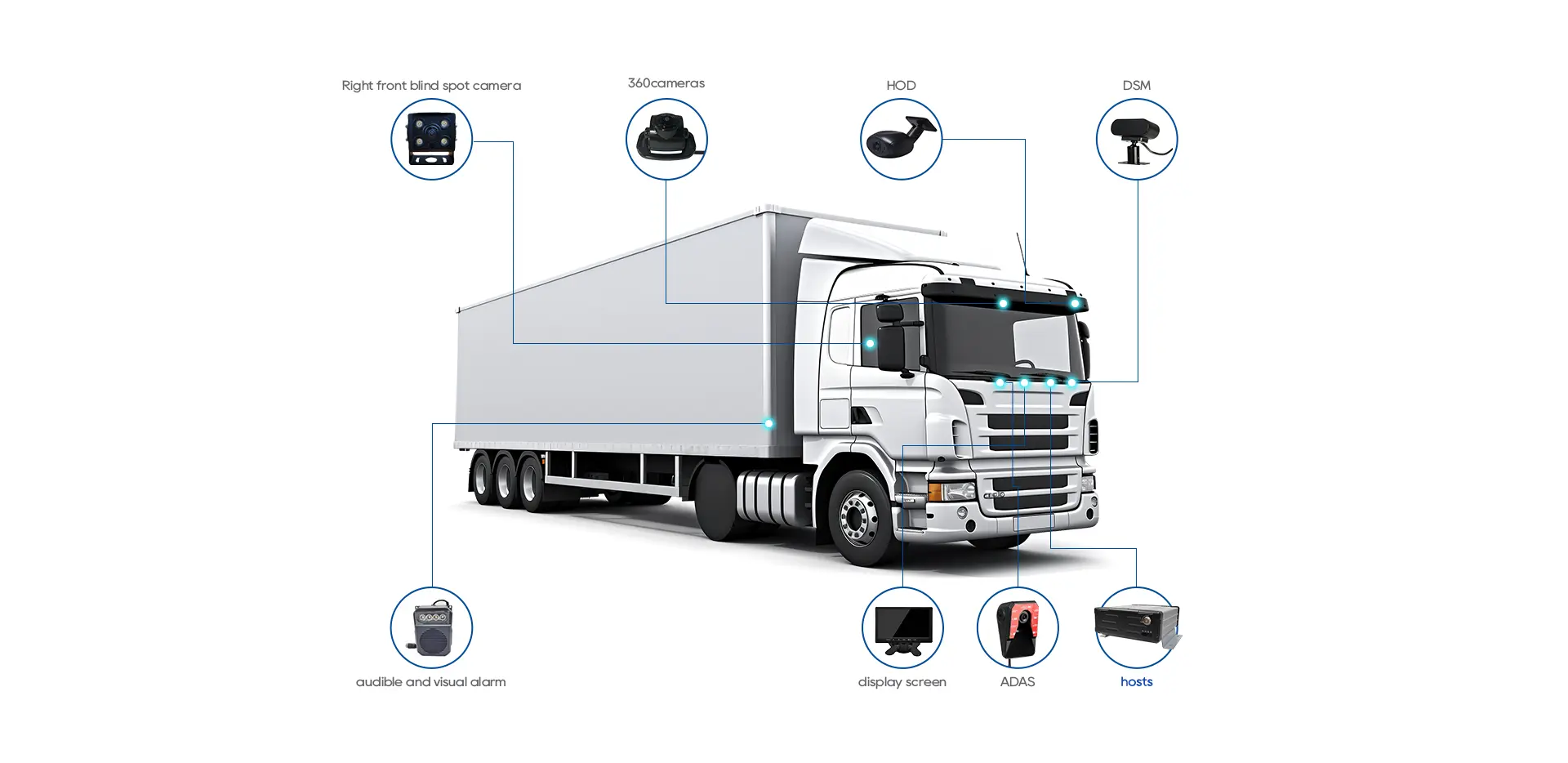
What is a Fleet Telematics System
Fleet Telematics Systems
Fleet telematics is an integrated solution driving the development of the automotive and transportation industries. Its core lies in collecting, transmitting, and analyzing data from vehicle remote devices via wireless technologies, thereby providing data support for fleet management.

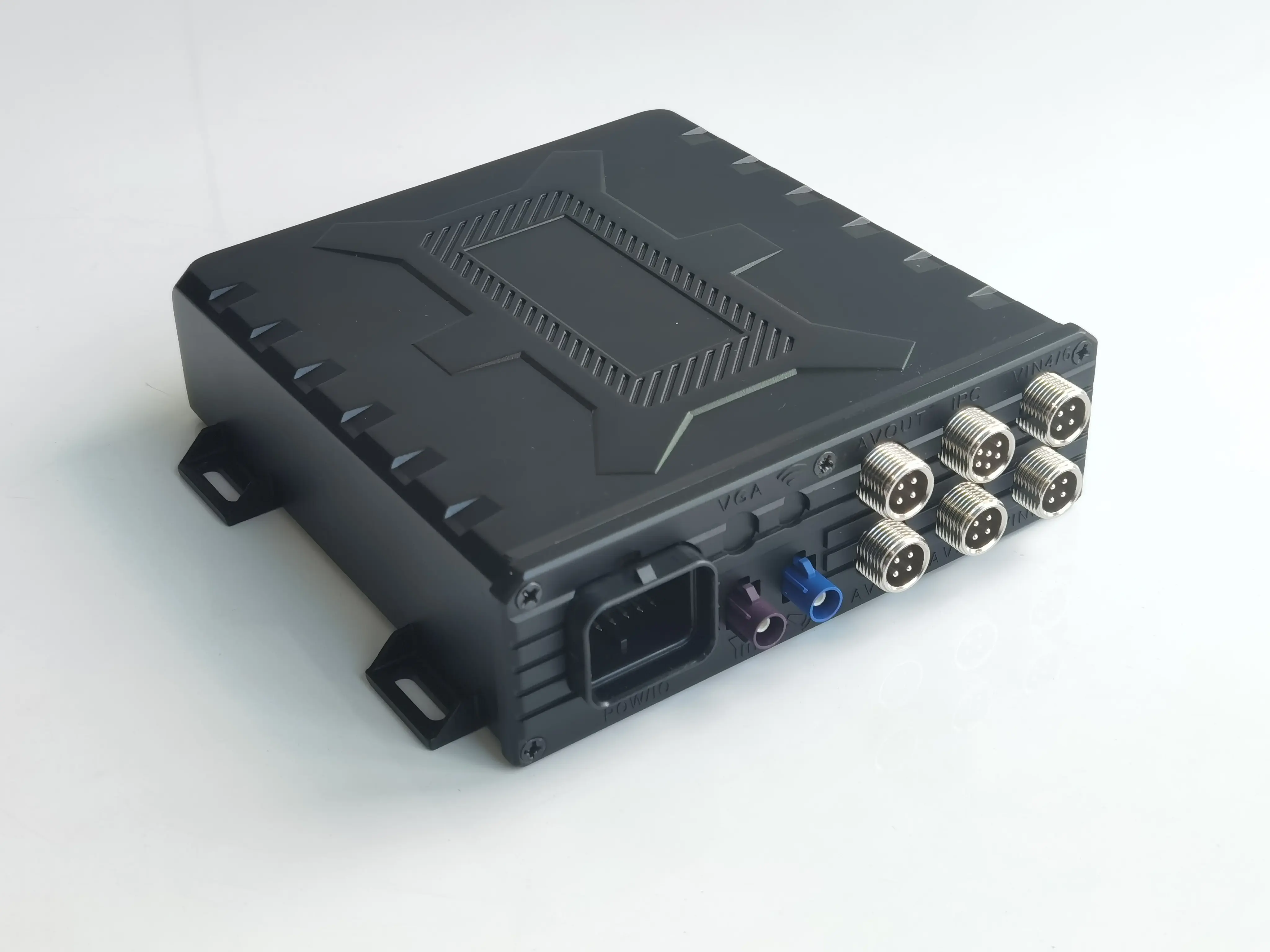
Components of a Fleet Telematics System
A telematics device consists of multiple key components to ensure the efficient operation of data throughout the entire process:
1. Hardware: Includes GPS receivers, accelerometers, OBD-II interfaces, and various sensors, capturing data on vehicle performance and driver behavior.
2. Connectivity Technologies: Relies on cellular networks, satellites, Bluetooth, etc., for data transmission. The selection of technologies should match requirements for transmission speed, coverage, and reliability.
3. Software & Analytics Platforms: Processes collected data, extracts insights, and generates reports to provide a basis for efficiency improvement, safety assurance, and decision optimization.
4. GPS Tracking: Achieves real-time and accurate vehicle positioning through GPS technology, facilitating optimal route planning.
5. On-Board Diagnostics (OBD): Monitors engine performance, fuel consumption, and vehicle speed, detects maintenance issues in a timely manner, and optimizes fuel efficiency.
6. Wireless Communication: Transmits vehicle data to fleet management systems via satellite communication and other technologies, enabling real-time global monitoring.
7. In-Vehicle Displays/Mobile Applications: Provide drivers with information such as navigation and safety alerts, balancing safety and efficiency.
8. Cloud-Based Software: Stores data in the cloud, allowing anytime, anywhere access with network connectivity.
9. Event-Triggered Alerts: Presets rules to automatically issue alerts in case of hard braking, speeding, engine faults, etc., supporting data-driven decision-making.
10. System Integration: Seamlessly interfaces with fleet management, maintenance management, and other systems.
11. Customized Reporting & Analysis: Simplifies the report generation process and can create exclusive reports tailored to fleet objectives.
Working Principles of Fleet Telematics
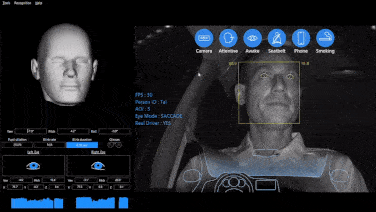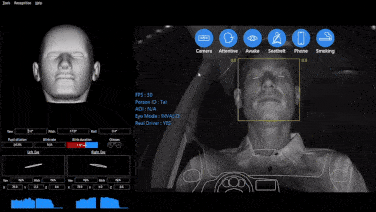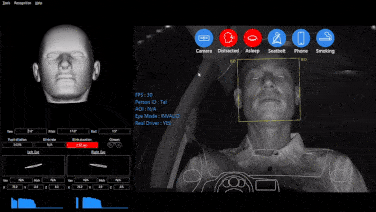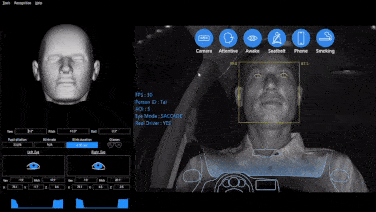
1. Data Collection: Devices installed in vehicles collect data from OBD, GPS receivers, and other sensors, covering vehicle location, driving duration, idling time, driving behavior, seat belt usage, fuel consumption, vehicle faults, etc.
2. Data Preprocessing: Data is transmitted to a central server or processed directly by the device, filtering out irrelevant information and formatting it to prepare for storage and analysis.
3. Data Transmission & Presentation: After interpretation and classification, data is transmitted to the cloud or central server via wireless technologies, synchronized to fleet management software, and presented in a clear and easy-to-understand format.
Application Scenarios
Telematics devices are widely used in multiple industries:
① Transportation & Logistics: Monitors vehicle location, fuel consumption, and driver behavior, optimizes routes, and improves customer service.
② Construction Industry: Tracks vehicle location in real time, identifies overtime work and inefficient operations, and optimizes scheduling and resource allocation.
③ Oil, Gas & Mining: Monitors driver service hours, ensures the compliant operation of enterprises, avoids penalties, and safeguards driver safety.
Core Advantages
It brings multiple significant values to fleet operation and management:
1. Reduce Fuel Costs: Analyzes fuel consumption and idling data, optimizes routes, reduces idling time, lowers fuel consumption, and minimizes environmental impact.
2. Enhance Safety Management: Monitors risky driving behaviors such as speeding and hard braking, guiding drivers to develop safe driving habits.
3. Simplify Maintenance Management: Receives real-time diagnostic data, arranges preventive maintenance in a timely manner, detects faults early, and reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
4. Optimize Customer Service: Tracks vehicles in real time, optimizes delivery routes, improves delivery efficiency, and enhances customer satisfaction.
5. Strengthen Fuel Management: Provides real-time data on fuel usage, identifies inefficiency issues and intervenes, improving fuel efficiency.
6. Simplify Compliance Management: Automatically tracks service hours and electronic log requirements, generates audit reports, reduces administrative burdens, and ensures compliance.
Telematics devices can optimize fleet management and drive enterprise transformation. To learn how fleet telematics systems can help your enterprise transform and build competitive advantages, welcome to contact YUWEI for consultation or a demo application.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com