Cold Chain IoT Telematics Solutions
Cold Chain IoT Solutions
Cold Chain IoT Telematics Solutions integrate the Internet of Things (IoT), telematics, and big data technologies to enable intelligent monitoring, management, and optimization across the entire cold chain process. The goal is to address traditional challenges—such as temperature loss of control, high spoilage rates, low efficiency, and difficulty in traceability—by leveraging real-time data to ensure the quality of perishable goods and reduce operational costs.

Key Pain Points of Traditional Cold Chain Systems
1. Manual temperature monitoringleads to delayed detection of “chain breaks,” resulting in product spoilage.
2. Limited traceabilitymakes it difficult to identify the responsible party after quality issues occur.
3. Experience-based vehicle dispatching and routinglead to high empty-load rates; equipment failures lack early warnings, causing delays.
4. Strict compliancerequirements in industries like pharmaceuticals and food are hard to meet with manual data entry, which is prone to tampering or omissions.
Core Technological Components
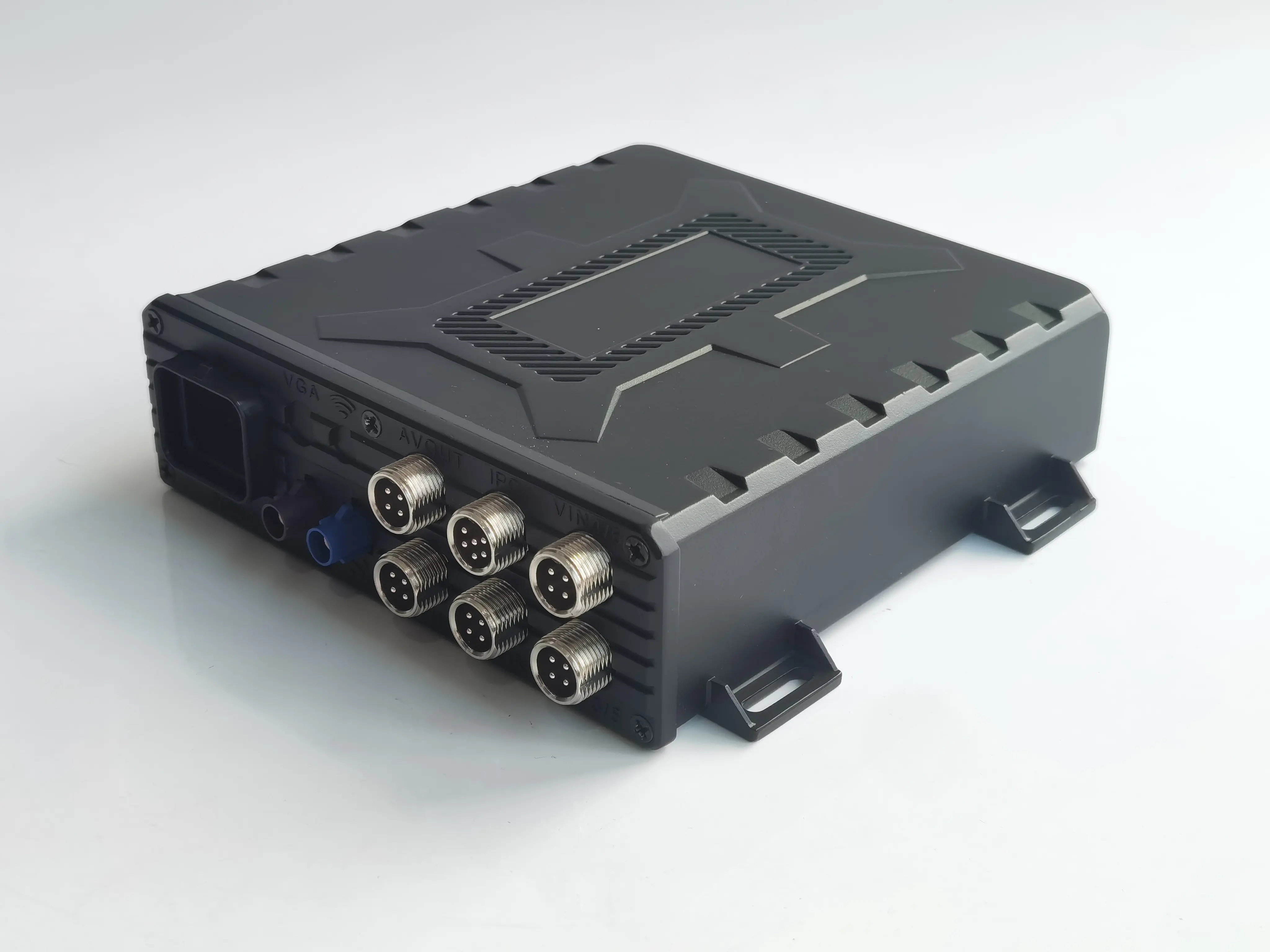
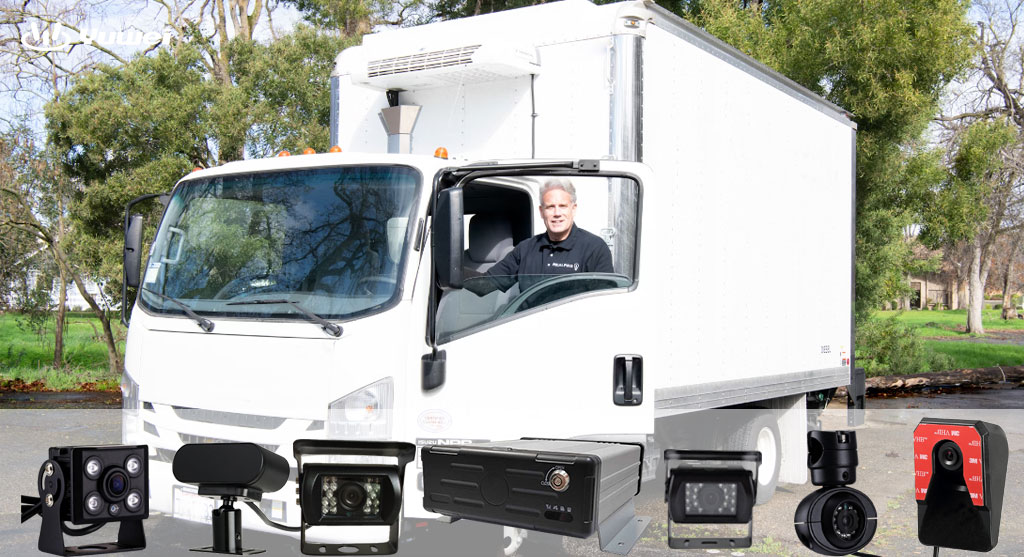
1. IoT Sensing Layer
a. Deploys sensors for temperature, humidity, GPS, door status, and vibration to collect real-time environmental data.
b. Onboard terminals and monitoring devices perform local preprocessing and encryption of data.
2. Telematics and Data Transmission
a. Utilizes 4G/5G, NB-IoT, and other communication technologies to ensure stable data transmission in complex environments.
b. Connects to vehicle OBD interfaces and CAN buses to access data such as speed and fuel consumption, enabling integrated monitoring of drivers, vehicles, cargo, and environment.
3. Data Processing and Application
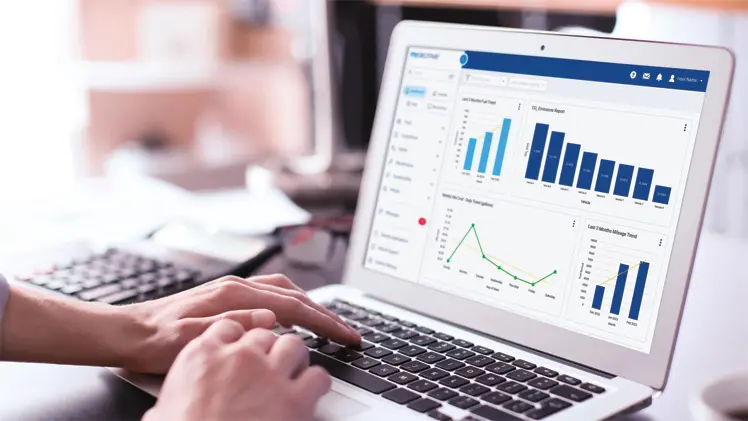
a. Cloud platforms receive and analyze massive data streams to generate temperature curves, alert reports, and visual dashboards.
b. AI algorithms predict temperature anomalies, provide early warnings for malfunctions, and optimize routing.
Core Value Propositions
1. Precision Temperature Control: Real-time monitoring triggers alerts once thresholds are exceeded, allowing timely intervention (e.g., 2–8°C compliance in pharmaceutical cold chains).
2. Transparent Traceability: Unique identifiers link cargo information to establish an end-to-end traceability chain, facilitating regulation and accountability.
3. Operational Efficiency: Smart dispatching reduces empty runs, predictive maintenance minimizes downtime, and inventory optimization avoids overstocking or shortages.
4. Data-Driven Decisions: Big data analytics highlight weak points (e.g., frequently problematic routes), supporting informed decision-making.
Typical Use Cases
1. Fresh Food: Monitor transport temperatures to prevent spoilage and ensure food safety through traceability.
2. Pharmaceuticals & Biologics: Provide compliant temperature logs and real-time alerts for vaccines, blood products, and more.
3. Cross-Border Logistics: Ensure uninterrupted long-distance data transmission via global positioning and satellite communication.
Future Trends
1. Integration of 5G and Edge Computing: Enhances real-time monitoring and control capabilities.
2. AI Empowerment: Optimizes temperature regulation strategies, predicts spoilage rates, and supports autonomous dispatch.
3. Blockchain for Data Integrity: Ensures tamper-proof data, strengthening trust across the supply chain.
4. Green and Low-Carbon Focus: Smart energy management reduces waste and supports sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion
This solution is central to the digital transformation of the cold chain. By shifting from “passive response” to “proactive prevention” through data-driven approaches, it not only ensures cargo safety but also boosts operational efficiency—making it a key pillar of the modern cold chain ecosystem.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com