Driver Safety Management System
What is a Driver Monitoring System?
In the process of intelligent transformation in the commercial vehicle sector, the Driver Monitoring System (DMS) has become a core component of autonomous driving technologies and advanced driver assistance systems.
As a key technical means to ensure driving safety, DMS can not only monitor the driver's condition in real time but also take appropriate intervention measures in critical moments to avoid accidents.

1. Definition and Background of DMS
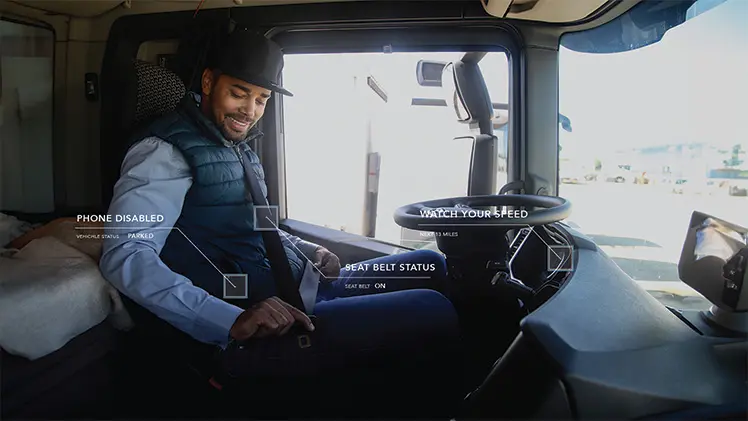
The Driver Monitoring System (DMS) is an advanced on-board safety technology that uses devices such as cameras and sensors to monitor the driver's behavior and status in real time, thereby ensuring that the driver remains alert and safe while driving.
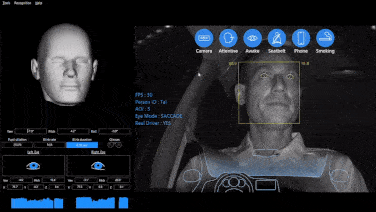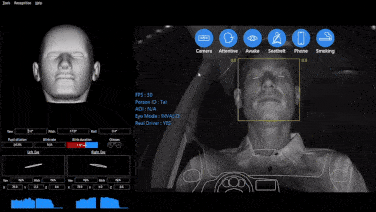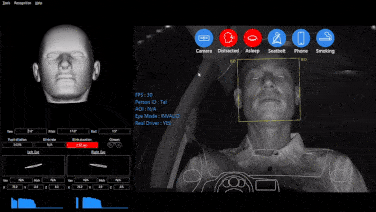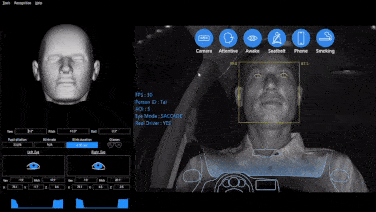
Initially, the main purpose of DMS was to monitor driver fatigue to prevent traffic accidents caused by drowsy driving. With the continuous development of machine vision technology, the functions of DMS have increased significantly. Today, it has evolved into a comprehensive system integrating fatigue detection, distracted driving detection, gaze detection, gesture recognition (for interaction with on-board systems), face recognition (for interaction with on-board systems), and expression recognition.
In commercial vehicles, freight vehicles, and special vehicles (such as school buses and emergency vehicles), the demand for DMS applications is more urgent. These vehicles often need to travel for long periods and bear significant responsibilities, and DMS can effectively prevent major accidents caused by driver fatigue or inattention.
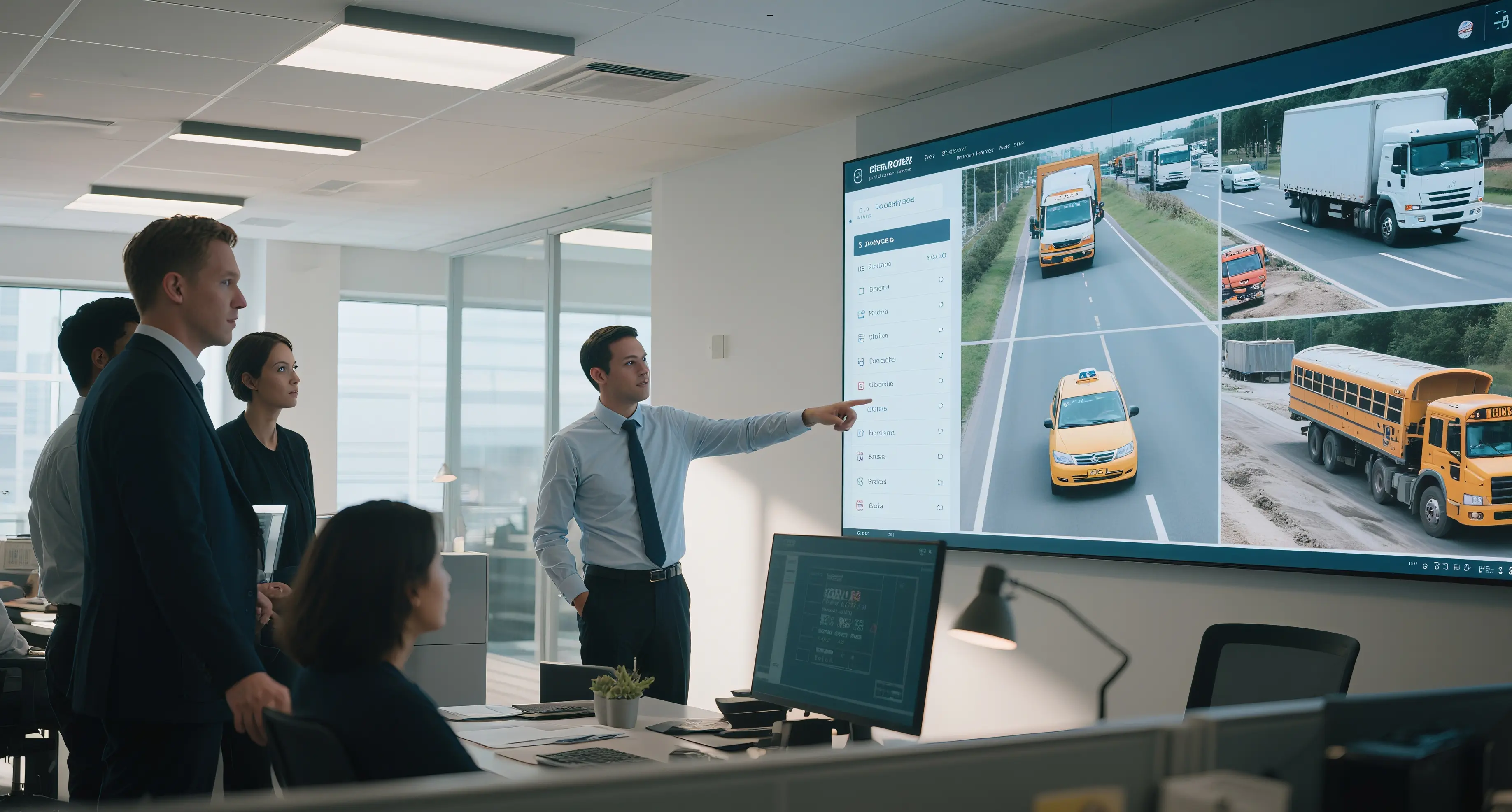
In addition, through the fleet management system, DMS can transmit the driver's status data to the background in real time, helping enterprises manage fleet operations more efficiently and reduce the possibility of accidents.
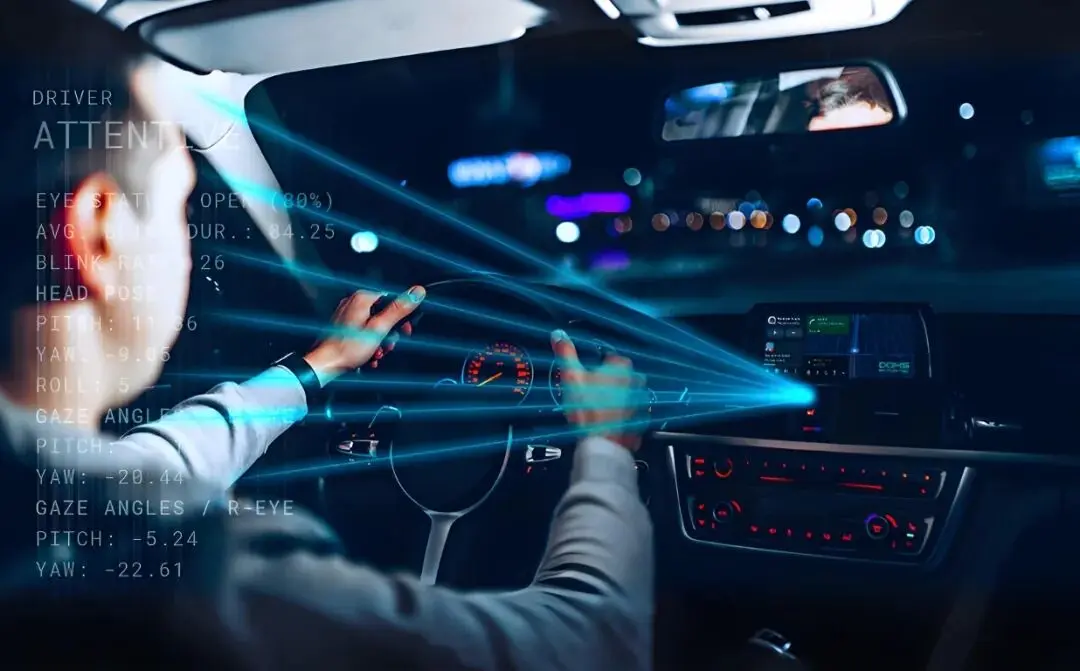

2. Technical Principles of DMS
According to the technical implementation principles, DMS (Driver Monitoring System) can be divided into two categories: passive DMS and active DMS. There are significant differences between the two in terms of core technical routes, applicable scenarios, and functional performance.
Passive DMS
It mainly relies on existing visual acquisition devices inside the vehicle (such as in-car cameras) to passively capture and analyze the driver's facial features and body movements through algorithms.
Its core principle is to use natural light or in-car ambient light without emitting additional signals. It only judges the driver's status through image recognition technology, such as monitoring eyelid closure frequency to identify fatigue, tracking gaze direction to determine the degree of inattention, or capturing dangerous actions such as yawning and looking down at mobile phones.
The advantages of this technical solution are low hardware costs, reusability with devices such as on-board surround-view cameras and cabin monitoring cameras, and no light or signal interference to the driver. It is suitable for vehicle models that are cost-sensitive and pursue lightweight deployment.
However, its performance is easily affected by ambient light. In environments with direct strong light, backlight, or darkness, the accuracy of image recognition may decrease, requiring continuous algorithm optimization to adapt to complex light conditions.

Active DMS
Active DMS adopts a technical route of actively emitting detection signals and receiving reflected information, with the most common being the infrared light technical solution.
The system emits infrared light of a specific wavelength to the driver's face through an infrared transmitter, and then a dedicated infrared camera receives the reflected light to construct a 3D model of the driver's face or dynamic feature data. Since infrared light is not affected by visible light, even in a completely dark environment, it can accurately capture details such as pupil changes, eye rotation angles, and facial muscle micro-expressions, thereby more reliably judging whether the driver is in a dangerous state such as drowsiness, distraction, or drunk driving.
Some high-end active DMS also incorporate technologies such as near-infrared spectroscopy analysis to further enhance the depth of physiological state monitoring, for example, using indicators such as heart rate and breathing frequency to assist in judging the driver's physical condition.
The advantages of this solution are strong environmental adaptability and higher recognition accuracy, especially suitable for complex scenarios such as night driving and tunnel passage. However, it requires additional infrared transmission and reception modules, resulting in relatively high hardware costs. It is usually applied to mid-to-high-end vehicle models or commercial vehicles with extreme safety performance requirements (such as long-distance trucks and dangerous goods transport vehicles).
From the perspective of development trends, passive DMS has become the mainstream choice for entry-level vehicle models due to its cost advantages, while active DMS is gradually penetrating the mid-end market with the improvement of technology maturity and cost reduction. Both are jointly promoting the popularization and upgrading of driver status monitoring technology.
With the widespread application of DMS, the privacy protection of driver data and the security of the system will become the focus of attention. For the field of advanced automotive safety driving systems, in-depth understanding and mastery of DMS technology will help occupy a technological high ground in the era of intelligent driving.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com