Geofencing Fleet Management
What is Geofencing for Fleet Management?
Geofencing is a virtual boundary technology based on Geographic Information System (GIS) and Location-Based Services (LBS). It allows managers to freely delineate electronic zones (i.e., "fences") of any shape on a map. When a GPS-equipped vehicle enters, exits, or moves within the zone, the system automatically triggers pre-set responses, such as issuing alerts or recording driving trajectories.
Compared with traditional electronic fences that rely on GPS to set simple shapes (e.g., circles, rectangles), geofencing can create more complex polygonal areas, catering to the management needs of intricate geographic environments like urban roads and industrial parks. Its core value lies in significantly enhancing the precision and efficiency of fleet management through real-time monitoring and automated early warnings.
Geofencing Application Scenarios
1. Transportation Route Monitoring & Compliance Management
① Practice: Predefine driving routes and stop points for critical tasks such as hazardous material transportation and oversized cargo logistics. The system triggers an immediate alert if a vehicle deviates from the designated route.
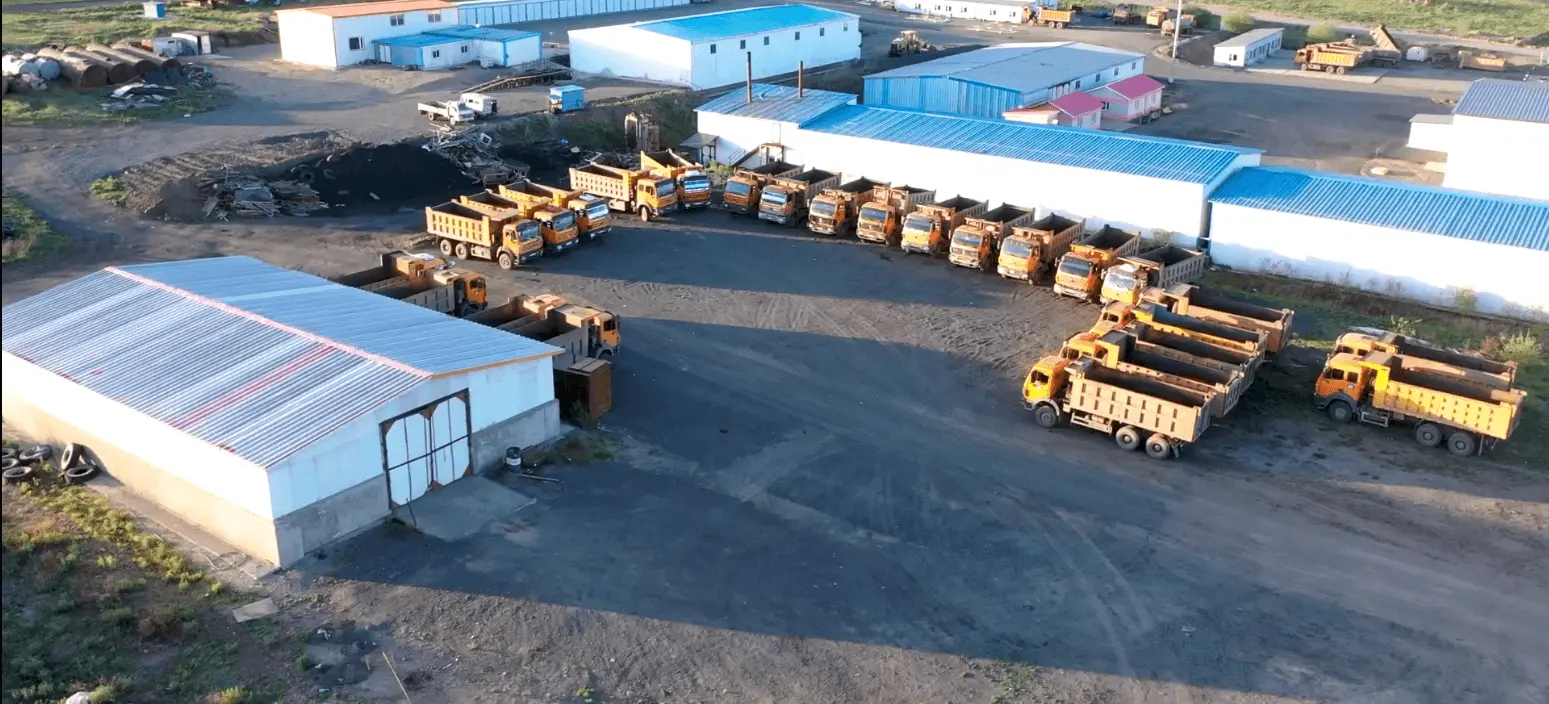
② Case: In the mining vehicle management project in Honghe Prefecture, delineating exclusive transportation routes and restricted hazardous zones effectively reduced the risk of vehicles straying into dangerous areas.
2. Vehicle Anti-theft & Asset Security
① Practice: Set up virtual boundaries around vehicle parking areas. During non-working hours, the system instantly sends alerts to managers if any vehicle is moved abnormally or driven out of the authorized zone.
② Value: Establishes a robust real-time anti-theft system, shortens response time to theft incidents, and increases the likelihood of asset recovery.
3. Fleet Operational Efficiency Optimization
① Practice: Managers can grasp the real-time location distribution of vehicles and task progress, enabling remote intelligent dispatching and optimized vehicle resource allocation.
② Case: A construction group deployed a geofencing system to centrally manage engineering vehicles scattered across multiple construction sites, improving management efficiency by over 50%.
4. Driving Behavior Monitoring & Safety Improvement
① Practice: Set speed-limited zones to monitor vehicle speed, sudden acceleration, and harsh braking within the fenced areas.
② Value: Data recorded by the system provides a basis for analyzing driver behavior, helping standardize driving habits, reduce accident rates, and support driver training and assessment.
Geofencing Solution
1. Core System Architecture
A typical geofencing system consists of the following components:
① On-board Terminal: Integrates GPS/Beidou positioning modules to collect real-time vehicle location data.
② Communication Network: Leverages mobile networks such as 5G to achieve high-speed, low-latency data transmission.
③ Data Processing Platform: The core "brain" of the system, responsible for processing location data, performing geofence matching calculations, and triggering rule-based responses.
④ User Interface: Usually a web or mobile application that visually displays vehicle positions, fence areas, and alarm information.
2. Dynamic Geofencing Technology
Traditional fixed fences have limitations in certain scenarios. The latest advancement is dynamic geofencing, which can automatically adjust the scope and center point of virtual boundaries based on changes in fleet formation and real-time road conditions (e.g., traffic congestion or accidents). For example, during the delivery of power supply materials, if the lead vehicle detects poor road conditions ahead, the system can dynamically re-plan the route and update the fence, ensuring the entire fleet adjusts its travel strategy efficiently and safely.
3. Key Implementation Steps
① Fence Delineation: Precisely draw fence boundaries on the map interface.
② Rule Setting: Define trigger conditions (entry/exit/stay) and corresponding actions (alarm/recording/notification).
③ Position Comparison: The system uses algorithms (e.g., point-in-polygon algorithm) to real-time determine the relationship between vehicle position and the geofence.
④ Event Triggering & Notification: When preset conditions are met, the system executes pre-defined actions and sends alerts to users.
Future Development Trends
① Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms will automatically learn and optimize fence boundaries and monitoring rules based on historical driving data, and even predict potential risks and issue early warnings.
② Deep Integration into the Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem: Geofencing will evolve from a standalone system to a fully connected component of intelligent transportation systems, linking with vehicle sensors, traffic signals, and smart road signs.
③ Combination with Digital Twin Technology: By creating virtual replicas of physical fleets and operational environments, managers can test various dispatching and emergency response strategies in a simulated setting, achieving higher-dimensional optimization.
Geofencing technology, through the creation of virtual boundaries, provides modern fleet management with powerful capabilities in real-time monitoring, automated early warning, and data analysis. It serves as a core tool for enhancing fleet safety, operational efficiency, and compliance.
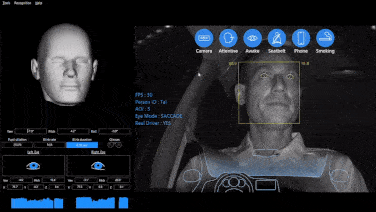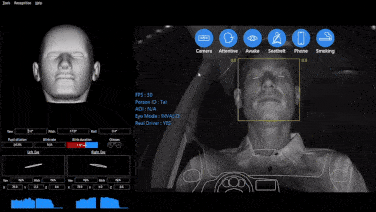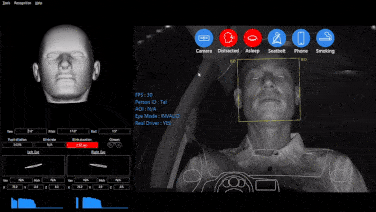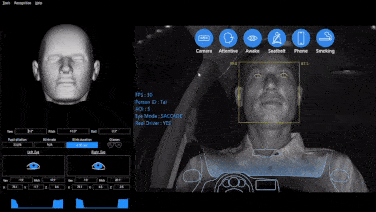
YUWEI’s commercial fleet tracking and management solution supports geofencing, GPS positioning, real-time monitoring, DMS monitoring, telematics, and other functions. Feel free to contact us for inquiries.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com