Fleet Telematics Solutions for Vehicle Tracking & Safety
What Is Telematics?
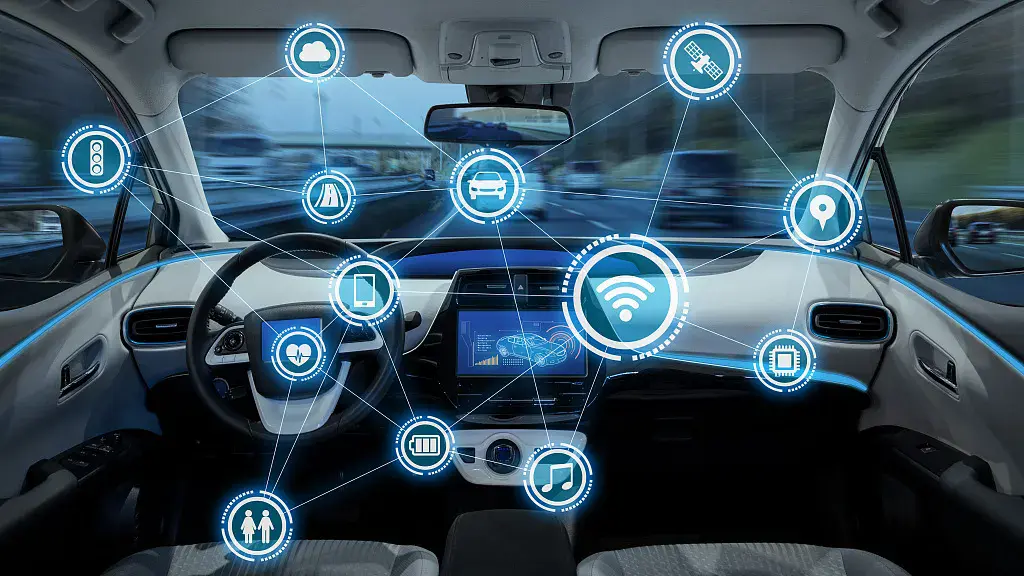
Telematics is an integrated technology combining telecommunications and information systems to monitor vehicles and assets in real time and provide operational insights. It collects, transmits, and analyzes data using cellular networks, GPS, sensors, and more—widely used in fleet operations today.

Introduction to Telematics
Telematics systems integrate On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) with wireless communication to deliver real-time data on vehicle location, performance, and driving behavior. This helps optimize operations, improve safety, and ensure compliance.
Types of Telematics
1. Fleet Telematics: Tracks vehicle usage, location, and status.
2. OEM Telematics: Built-in systems provided by manufacturers (e.g., YUWEI Telematics).
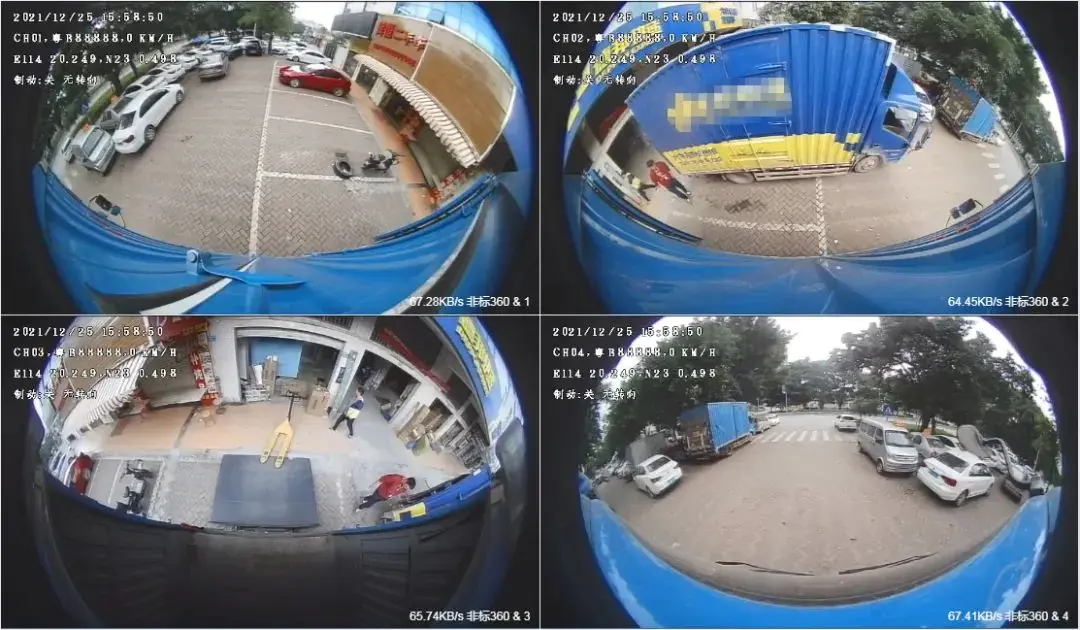
3. Video Telematics: Combines vehicle cameras to record driving behavior.
4. Asset Tracking: Monitors non-vehicle assets like machinery and equipment.
5. Insurance Telematics: Helps insurers assess risk and adjust premiums.
6. Automotive Insurance Telematics: Known as “black boxes,” used to monitor driver behavior.
Fleet Tracking vs. Fleet Telematics
1. Fleet Tracking: Focuses on “Where is the vehicle?” via GPS and route data.
2. Telematics: Broader scope—covers driving behavior, fuel usage, maintenance alerts, and more.
In short, tracking is a subset of telematics, which offers a holistic view of fleet operations.
How Telematics Systems Work: Four Core Components
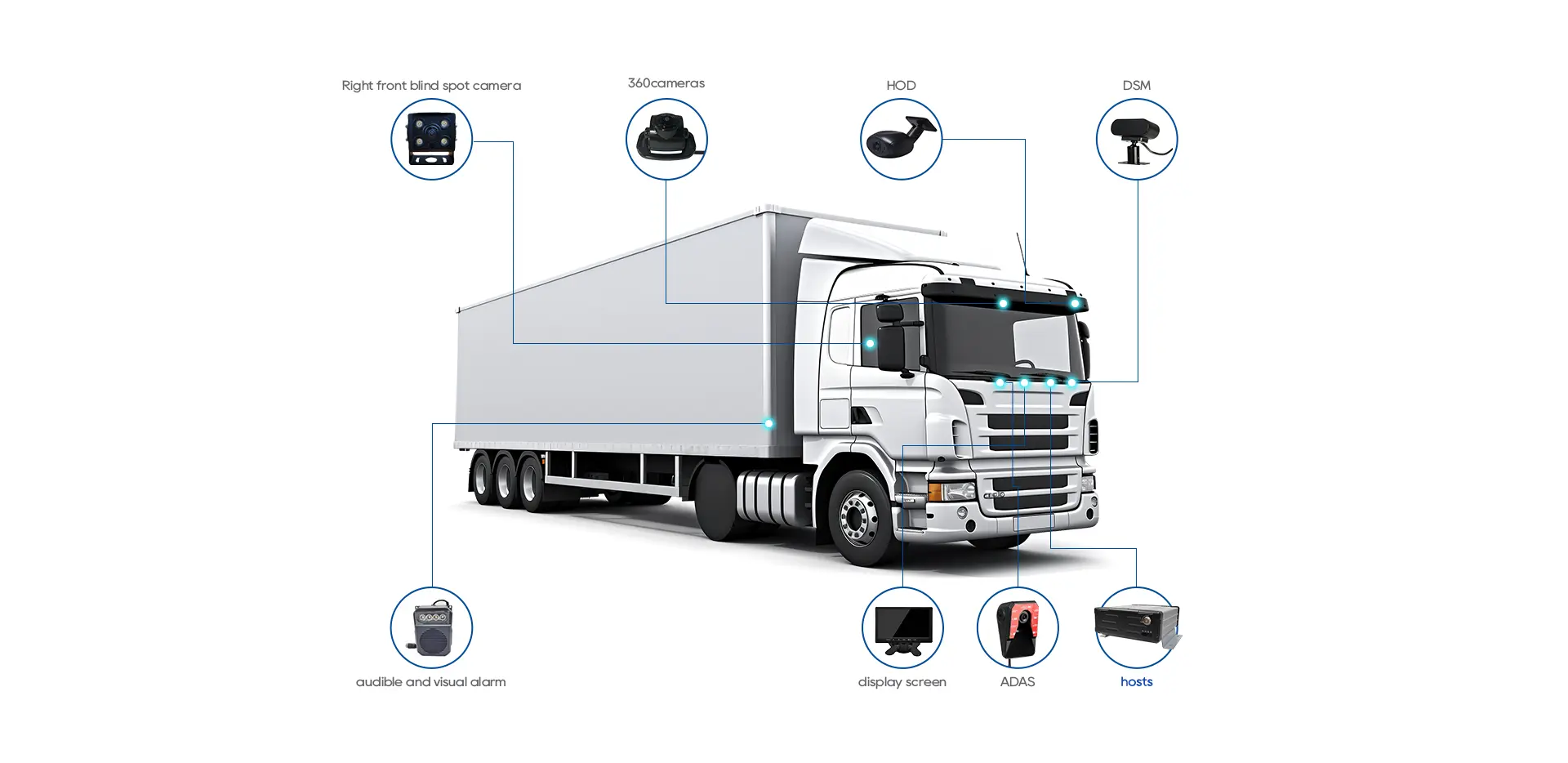
1. Hardware
Includes GPS trackers, OBD devices, sensors, cameras, TPMS, black boxes, etc.
2. Data Transmission & Collection
Data such as speed, engine diagnostics, driving behavior, and video are transmitted via cellular or satellite networks.
3. Management Software
Visualizes data, generates automated alerts, and delivers insights to aid decision-making and management optimization.
4. Installation
Professional installation ensures stable power, accurate data, and a seamless user experience.
System Integration Methods
1. OEM Integration: Pre-installed by manufacturers in new vehicles.
2. Aftermarket Systems: Installed by third-party professionals with custom setups.
Both options offer benefits—aftermarket systems often provide greater flexibility and third-party feature support.
Applicable Vehicles & Assets
Telematics systems can be used with:
1. Motorcycles, cars, trucks
2. Airport vehicles
3. Construction equipment (excavators, cranes, etc.)
4. Heavy industrial assets (generators, lighting systems, etc.)
Telematics vs. GPS Tracking
1. GPS Tracking: Locates vehicles.
2. Telematics: Offers comprehensive insights into vehicle condition, driver behavior, and maintenance.
GPS tracking is a foundational part of telematics; telematics enables deeper analysis and optimization.
How Telematics Data Optimizes Fleet Operations
Data collected by telematics can be used to:
1. Optimize routes and fuel consumption
2. Manage tire pressure and temperature
3. Support fleet electrification decisions
4. Digitize operations and reduce paperwork
Who Uses Telematics?
Telematics is widely used across various industries:
1. Public safety (police cars, ambulances, etc.)
2. Transportation & logistics
3. Construction
4. Car sharing & rental services
5. Utilities & field services
Benefits of Telematics
For fleet operators:
1. Real-time data supports better decision-making
2. Reduces fuel and maintenance costs
3. Enables compliance and automated reporting
For drivers:
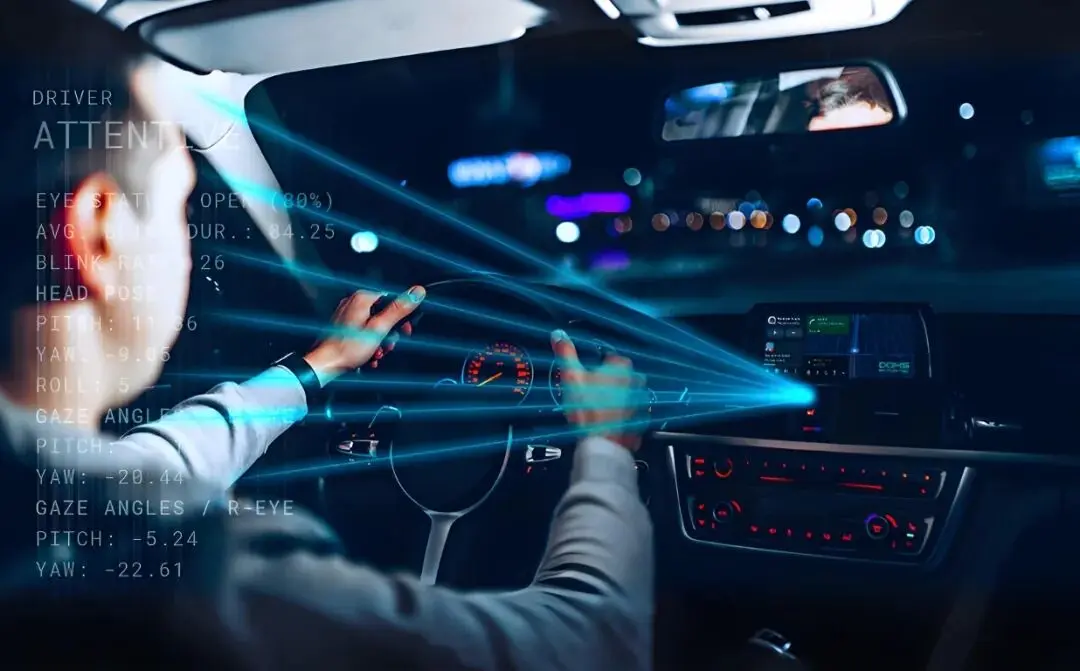
1. Improves road safety
2. Reduces driver fatigue
3. Provides better navigation and feedback
Technological Advances & Trends
Modern telematics has evolved from simple tracking to full-stack integrated solutions, incorporating AI, video analytics, TPMS, and more. Fleet managers can start with basic functions and scale up to build systems tailored to their specific needs.
More:best 4 channel dash cam | 360 camera for semi truck | mini adas dashcam | truck cctv surveillance camera | ldws dash cam