Telematics Definition, Meaning, Technology & Vehicle Systems
Telematics Vehicle Systems
Telematics is the integration of telecommunications technology, vehicle technology, and computer science.
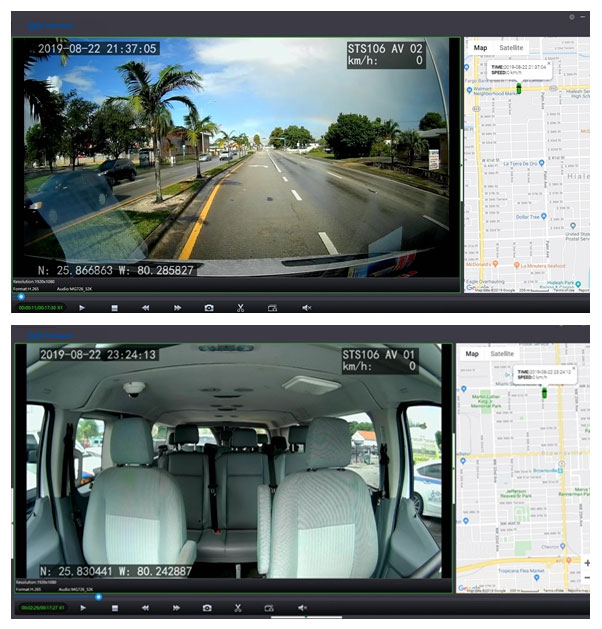
At its core are vehicle-mounted tools—typically using GPS and onboard computers to capture data such as vehicle speed, location, fuel efficiency, and driver service hours—then transmitting this data to a fleet tracking system for analysis.
It helps fleet managers meet compliance requirements (such as the Electronic Logging Device (ELD) mandate), improve fuel efficiency, enable predictive maintenance, enhance driver safety (reducing accident rates), and lower insurance costs.
In the future, with the convergence of 5G, artificial intelligence, and big data, its applications will continue to expand.

Definition and Meaning of Telematics
1. What is Telematics?
Telematicsis the combination of Telecommunicationsand Informatics, referring to the use of wireless communication technologies (such as cellular networks, GPS, Wi-Fi, etc.) to collect, transmit, and process data for remote monitoring, diagnostics, and management.
2. Definition of Telematics
According to industry definitions, Telematicsrefers to:
“Using communication technologies and computer systems to remotely collect, transmit, and analyze data from vehicles, equipment, or assets to optimize operations, enhance safety, and improve user experience.”
In simple terms, it is not just GPS tracking, but also includes vehicle diagnostics, remote control, fleet management, and emergency assistance.
3. Meaning of Telematics
① Data-Driven Decision Making: Collecting vehicle operation data (such as speed, fuel consumption, location) to help businesses and individuals make smarter decisions.
② Intelligent Connectivity: Enabling vehicles, devices, and infrastructure to communicate with each other, forming the Internet of Vehicles (IoV).
③ Automated Management: Reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency, such as automatic fault alerts and remote software updates.
Telematics Technology and Vehicle Systems
1. Telematics Technology
Telematics technologycovers multiple areas, including:
① GPS / GNSS Positioning: Real-time tracking of vehicle or asset location.
② Cellular Communication (4G/5G): Enabling remote data transmission.
③ Sensor Technology: Monitoring key parameters such as speed, fuel level, and tire pressure.
④ Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics: Storing and analyzing massive amounts of data to optimize operations.
⑤ On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II): Reading vehicle fault codes and predicting maintenance needs.
2. Telematics System
A Telematics Systemtypically consists of the following components:
1. T-BOX (Telematics Control Unit): The core device responsible for data collection and communication.
2. Vehicle Sensors: Monitor vehicle conditions (such as engine, battery, and brakes).
3. Communication Module: Transmits data via 4G/5G, NB-IoT, or LoRa.
4. Cloud Platform: Stores and analyzes data, providing a visual interface.
5. User Terminal: Such as mobile apps or web dashboards for viewing and management.
3. What is Vehicle Telematics?
Vehicle Telematicsis the application of telematics in the automotive field, mainly including:
① Fleet Management: Monitoring multiple vehicles’ locations, fuel consumption, and driving behavior.
② Emergency Assistance: Such as eCall (automatic accident alert).
③ Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): Adjusting insurance premiums based on driving habits.
④ Remote Control: For example, remote unlocking or engine start.
Telematics Devices and Solutions
1. What is a Telematics Device?
Telematics devicesinclude:
① T-BOX (Telematics Control Unit): The core equipment responsible for data transmission.
② GPS Tracker: For asset or vehicle positioning.
③ OBD-II Adapter: Connects to the vehicle diagnostic interface to obtain real-time data.
④ Smart Vehicle Terminal: Integrates entertainment, navigation, and remote communication functions.
2. What is a Telematics Solution?
Telematics solutionsare typically tailored to different industries, such as:
① Commercial Fleet Management: Route optimization and fuel reduction.
② Insurance Industry: Driving data-based Usage-Based Insurance (UBI).
③ Smart Cities: Intelligent parking and traffic flow monitoring.
④ Logistics & Transportation: Real-time cargo tracking and delivery efficiency improvement.
YUWEI’s Three High-Performance T-BOX Telematics Devices
If you are looking for reliable telematics devices, YUWEIoffers three industry-leading T-BOX solutionssuitable for automobiles, commercial fleets, and asset tracking.
1. YUWEI AI (Smart T-BOX)
① Supports 4G/5G Communicationfor high-speed data transmission.
② Integrated GPS + BeiDou Dual-Mode Positioningfor precise tracking.
③ Supports Remote Diagnostics and OTA Upgrades.
④ Ideal for Intelligent Connected Vehicles and New Energy Vehicles.
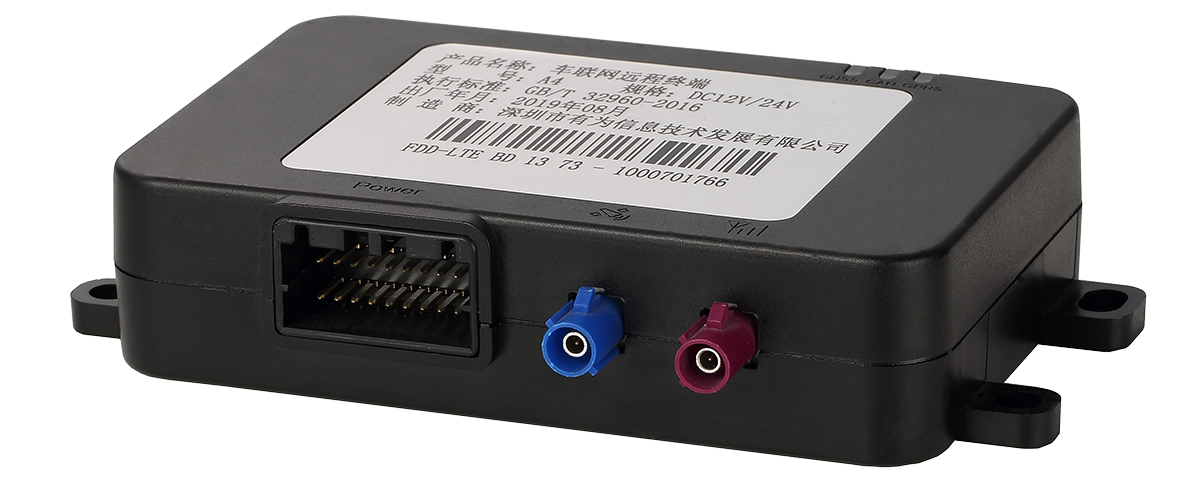
2. YUWEI A4 (Multi-Function Telematics Device)
① Lightweight Designfor easy installation.
② Supports OBD-II Interfaceto read real-time vehicle data.
③ Suitable for Fleet Management and Rental Industries.
④ Low Power Consumption with Long Battery Life.
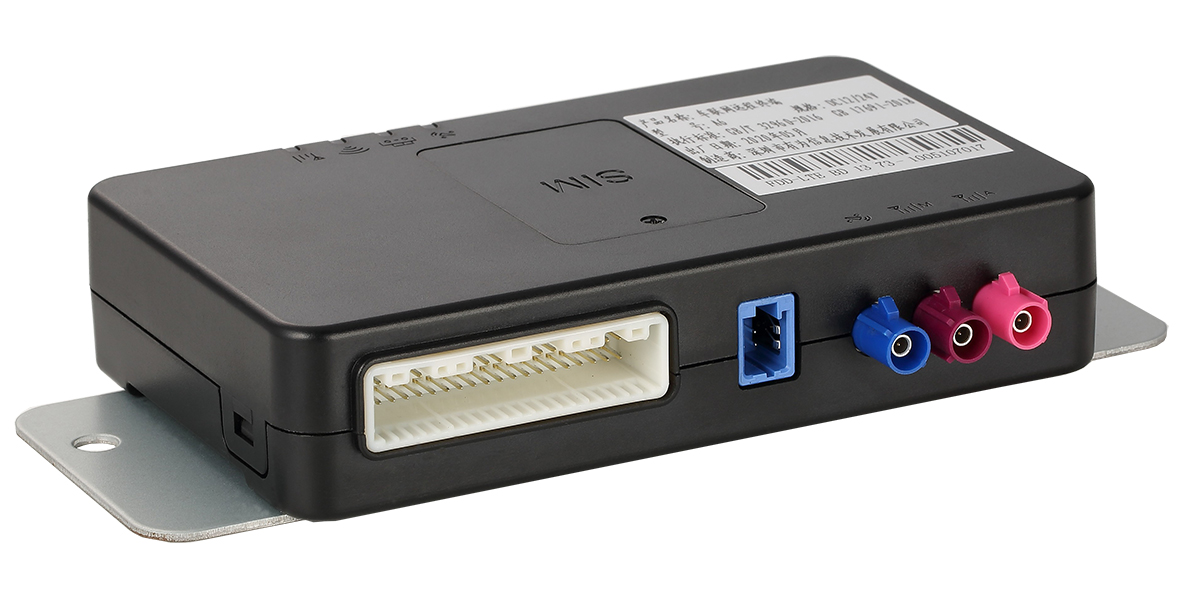
3. YUWEI A6 (High-End TCU – Telematics Control Unit)
① Industrial-Grade Stabilityfor harsh environments.
② Supports Multiple Communication Protocols (CAN, LIN, Ethernet).
③ Suitable for Commercial Vehicles and Special-Purpose Vehicles.
④ Provides Customized Solutions.
If you are seeking reliable telematics devices, YUWEI’s AI, A4, and A6 T-BOXare trusted choices, suitable for automotive, logistics, and insuranceindustries.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com