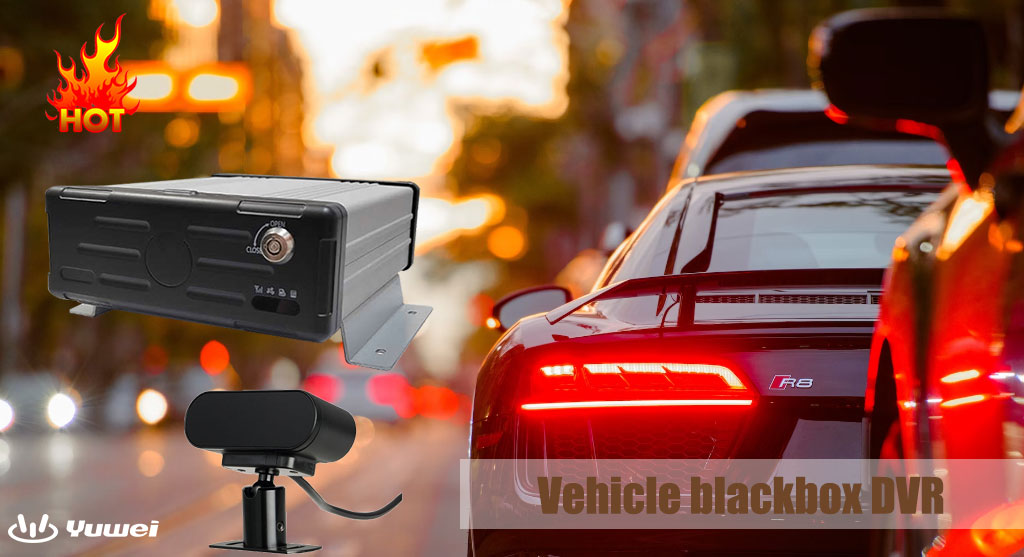
Telematics Vehicle Drive Recorders help protect Fleet safety
Telematics and Vehicle Drive Recorder Collaboration
With advancements in technology, the new generation of vehicle drive recorders differs from their predecessors. In the past, drive recorders typically stored videos on memory cards, requiring drivers to extract videos when needed. However, the new generation of drive recorders not only store videos on memory cards but also synchronize them to cloud servers through telematics technology.

Telematics devices can retrieve data from drive recorders, such as GPS location, speed, engine light information, and faults. Additionally, built-in accelerometers in the devices can measure G-forces. The telematics devices then send this data to the cloud. Through telematics devices and other connected hardware or sensors, a large amount of data, including location, vehicle speed, trip distance, and other engine data, can be processed and analyzed. Finally, this data is decoded and input into fleet management platforms for reporting and analysis.
Benefits of combining drive recorders and telematics
Traffic accidents are often unpredictable. According to statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States, approximately 8 people die each day due to accidents caused by distracted drivers. These accidents can result in damage to a company's reputation, significant insurance liabilities, and expensive repair costs, especially when there are no other witnesses and no verifiable evidence of driver behavior or intent.
However, with the help of reliable drive recorders and telematics, journey recordings of drivers can be uploaded to the cloud, allowing fleet managers to view videos and image data at any time. When a traffic accident occurs, fleet managers can extract videos from the drive recorders to understand the specifics of the accident and use the video as evidence to safeguard driver safety and the fleet's interests.
The useful data provided by reliable drive recorders allows fleet managers to monitor the driving status and behavior of each vehicle in real-time, contributing to improved fleet operations and efficiency. Furthermore, telematics can analyze the collected data to provide fleet managers with better insights into various aspects of the fleet, such as driver behavior, vehicle maintenance, potential hazards, and fuel usage. Data analysis also offers further utilization of telematics, for example, fleets can use benchmark testing to understand how their fleet performs in terms of safety compared to similar fleets or assess whether routes are optimized.
Principles of telematics and drive recorders
1. Data collection: Drive recorders collect real-time data during vehicle operation, including video, location, speed, acceleration, etc., through built-in cameras, GPS receivers, accelerometers, and other sensors.
2. Data storage: The collected data is stored in the internal memory or external storage cards of the drive recorder. Additionally, the new generation of drive recorders supports synchronizing data to cloud servers through telematics technology.
3. Data transmission: Drive recorders transmit data to remote telematics devices via wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or mobile networks. These devices can be fleet management platforms, cloud servers, or other terminal devices.
4. Remote information processing: After receiving the transmitted data from drive recorders, remote telematics devices decode and process the data. This includes video decoding, location tracking, speed calculation, acceleration analysis, and other operations.
5. Data analysis and application: Processed data can undergo further analysis and application. For example, video analysis can detect driver behaviors such as speeding, lane changing, and braking; location and speed data can be used for route planning and driving efficiency evaluation; acceleration data can identify vehicle vibrations and collisions.
6. Data visualization and reporting: Processed data can be presented to fleet managers or drivers in visual forms such as real-time monitoring interfaces, report charts, and alert notifications. This helps them understand vehicle status, driving behavior, and potential risks.
Conclusion
The combination of telematics and high-quality drive recorders brings many benefits, including reduced operating costs, improved fuel efficiency, and productivity. Specifically, video telematics enhances safety by providing greater visibility, helping businesses enhance fleet operations.