Commercial Fleet Vehicle Camera Buying Guide
Commercial Fleet Vehicle Camera Buying Guide
In today’s transportation industry, vehicle cameras are becoming increasingly essential. They enhance safety, simplify operations, improve situational awareness, and play a vital role in the advancement of autonomous driving. From parking assistance to blind spot detection and complex automated driving functions, cameras—integrated with other technologies—are driving the transformation of the automotive sector.

Common Types of Vehicle Cameras
Rearview Camera
1. Provides a clear view behind the vehicle to prevent collisions
2. Features: wide-angle lens, low-light night vision, parking guide lines
3. Installation: mounted near the rear license plate or bumper
Front Camera
1. Assists with detecting obstacles and navigating tight spaces
2. Features: high-resolution imaging, ADAS integration
3. Installation: front grille or bumper
Dash Camera
1. Records incidents, supports insurance claims, monitors road conditions
2. Features: continuous loop recording, G-sensor impact lock, GPS tracking
3. Installation: windshield or dashboard
Side Camera
1. Eliminates blind spots, assists with lane changes
2. Features: real-time side view display, wide-angle lens
3. Installation: side mirrors or vehicle side panels
360-Degree Surround View Camera
1. Provides a bird’s-eye view of the vehicle for easier parking
2. Features: image stitching from multiple cameras, obstacle detection
3. Installation: front, rear, and sides of the vehicle
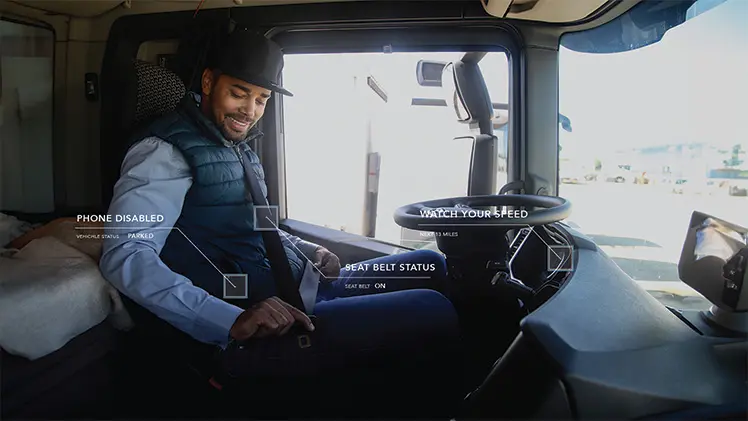
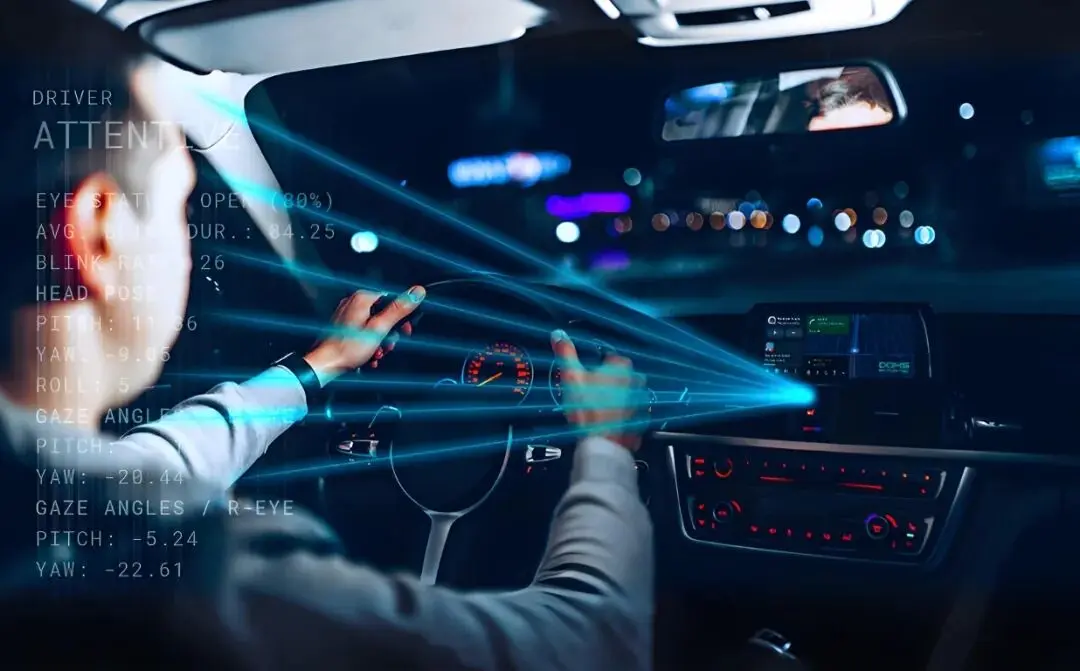
Interior Camera
1. Monitors driver and passengers
2. Features: infrared night vision, optional two-way communication
3. Installation: dashboard or ceiling
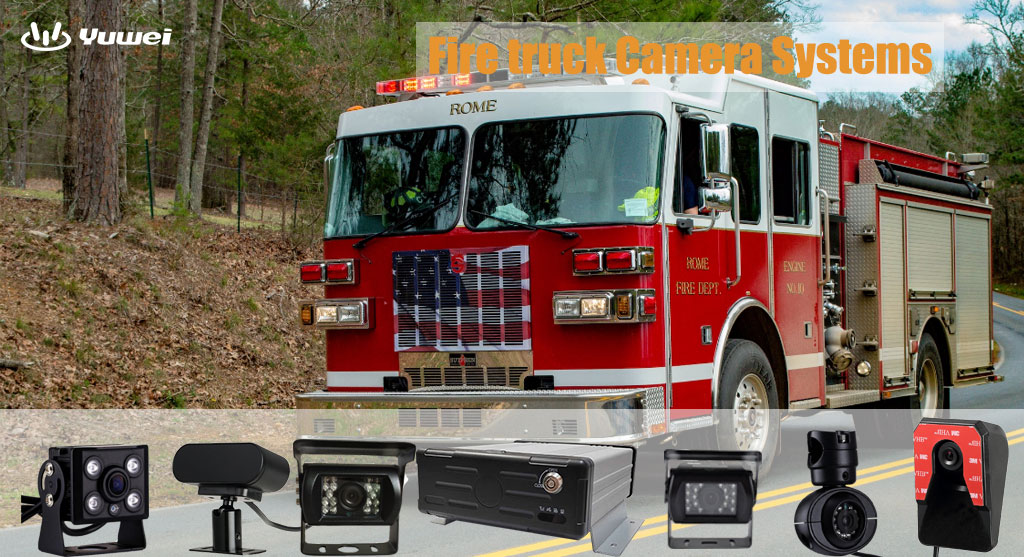
Trailer Camera
1. Helps monitor trailers for safer handling and maneuvering
2. Features: weatherproof design, wireless connectivity
3. Installation: rear or side of trailer
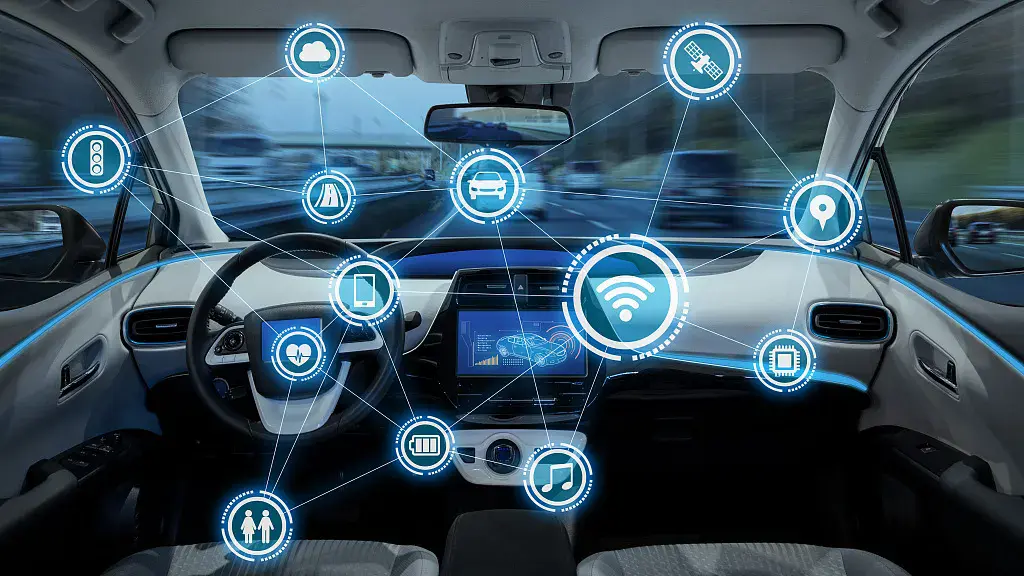
Camera Applications in Autonomous Driving
Vehicle cameras work alongside sensors such as LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to enable:
1. Lane detection and road marking recognition
2. Detection of pedestrians, vehicles, bicycles, and other objects
3. Traffic sign recognition and adaptive response
4. Surround view for parking assistance
5. Driver fatigue and distraction monitoring
The combination of multiple cameras and sensor fusion is key to intelligent driving systems.
Installation Guide
1. Prepare tools: screwdriver, adhesive mounts, electrical tape, wire connectors
2. Select the right positions: ensure clear, unobstructed views for each camera
3. Secure the cameras: firmly install using screws or mounts
4. Conceal wiring: route wires behind trim panels or carpets for a neat look
5. Power connection: connect to the fuse box or a 12V outlet
6. Calibrate and test: adjust angles for clear views and verify functionality
Recommended Camera Configurations by Vehicle Type
1.Passenger Car
Rearview camera + dash camera (optional side cameras)
2.SUV / Pickup Truck
Rearview + dash camera + side cameras + optional front camera
3.Commercial / Fleet Vehicle
Rearview + dash camera + side cameras + interior camera
4.Trailer / RV
Rearview + dash camera + side cameras + trailer camera + front camera
5.Autonomous Vehicle
Rearview + dash camera + side cameras + interior camera + 360 surround view + ADAS-specific cameras
Maintenance Tips
1. Regularly clean lenses with a microfiber cloth
2. Check cable connections to ensure they’re secure
3. Keep firmware up to date for best performance
4. Inspect mounts to confirm stability and proper alignment
Vehicle cameras are at the core of modern automotive intelligence and safety. Since 1998, YUWEIhas played an important role in building safer and smarter mobility solutions—and will continue to do so as transportation technology evolves.
Email:hello@yuweitek.com
More:adas camera | fleet dash cam | black box traffic recorder | school bus tracking system