What is a BSD (Blind Spot Detection) System?
Blind Spot Detection System (BSD)
According to the latest data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Traffic Safety Facts Report, more than 6.1 million traffic accidents occurred in the United States in the past year, resulting in nearly 43,000 deaths and approximately 2.5 million injuries. This underscores the urgent need for continuous improvement in road safety measures.

What is a Blind Spot?
A blind spot refers to areas that the driver cannot see using only the rearview mirrors. These blind spots are usually caused by structural parts (such as the A-pillars, the column between the windshield and side windows) or any objects that obstruct the driver's line of sight. Eliminating these blind spots can significantly improve driving safety. The solution is: Blind Spot Detection System (BSD), a technology designed to alert drivers to vehicles or obstacles in these unseen areas, thus significantly enhancing road safety.
Introduction to the Blind Spot Detection System (BSD)
Blind Spot Detection (BSD) systems are driving assistance features that help prevent collisions when changing lanes. By alerting drivers to vehicles in the blind spot (on the right or left, areas not visible in the rearview mirror), these systems effectively reduce the risk of accidents. The system uses sensors or cameras to detect vehicles in adjacent lanes and warns the driver with visual or auditory signals.
Different car manufacturers have different names for this technology:
- Toyota: Blind Spot Monitor (BSM)
- Hyundai: Blind-Spot Collision Warning (BCW)
- Volvo: Blind Spot Information System (BLIS)
- Mazda: Rear Vehicle Monitoring (RVM)
Although the names differ, the common goal of these systems is to enhance driver safety by reducing lane-change accidents caused by blind spots.
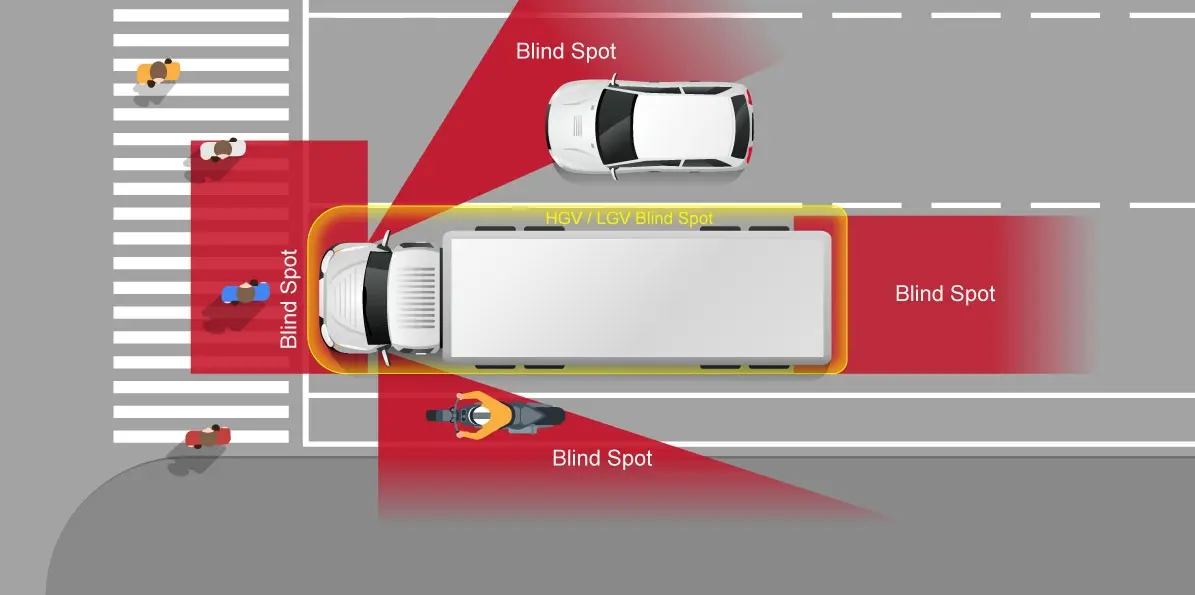
Types of Blind Spots in Trucks
Trucks have multiple blind spots that can reduce the driver’s visibility of the surrounding environment, potentially posing risks to other road users. The primary blind spots include:
1. Front Blind Spot: Extending several feet in front of the truck cabin, shorter vehicles may be completely hidden from the driver's view.
2. Side Blind Spot: The blind areas on either side of the truck, where smaller vehicles may disappear from view, particularly on the right side.
3. Rear Blind Spot: The significant blind spot directly behind the truck's trailer, where vehicles close behind may go unnoticed.
How Does the Blind Spot Detection System Work?
The Blind Spot Detection (BSD) system uses radar sensors and cameras to monitor the vehicle's surroundings and detect objects in blind spots. The system relies on radar technology to detect the presence of vehicles, cyclists, or pedestrians within a specified range around the vehicle, typically covering areas that side mirrors and rearview mirrors may miss.
When an object enters a blind spot, the system triggers an alert, usually a visual warning (such as an indicator light in the side mirror) or an auditory warning (such as a sound signal inside the cabin). Some advanced BSD systems are also equipped with automatic braking or steering assist features to help drivers avoid potential collisions.
BSD System Recommendations
The YUWEI Blind Spot Detection (BSD) system typically includes multi-directional monitoring of front, left, right, and rear blind spots.
Pedestrian Recognition Requirements
- It should support the detection of pedestrians in the right-side blind spot, including pedestrians on foot, electric scooter riders, cyclists, etc., and distinguish between pedestrians and regular obstacles.
- It should be able to recognize pedestrians taller than 80 cm.
- The pedestrian monitoring function for the right-side blind spot should continue working when the vehicle's ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control) is activated.
Monitoring Range Requirements
- It should monitor pedestrians within 300 cm to the right of the vehicle.
- It should monitor pedestrians from the center of the mid-bridge to 200 cm in front of the vehicle's windshield.
Recognition Accuracy Requirements
- The pedestrian recognition accuracy during the day should be at least 95%.
- The pedestrian recognition accuracy at night should be at least 90%.
Collision Warning Requirements
- When the pedestrian is within 300 cm of the vehicle’s right side, a Level 3 collision warning should be triggered.
- When the pedestrian is within 200 cm of the vehicle’s right side, a Level 2 collision warning should be triggered.
- When the pedestrian is within 100 cm of the vehicle’s right side, a Level 1 collision warning should be triggered.
Supporting Products for the Blind Spot Detection System
YUWEI offers a variety of BSD monitoring products, including different types of high-definition waterproof cameras to meet the blind spot monitoring needs for various vehicle positions:
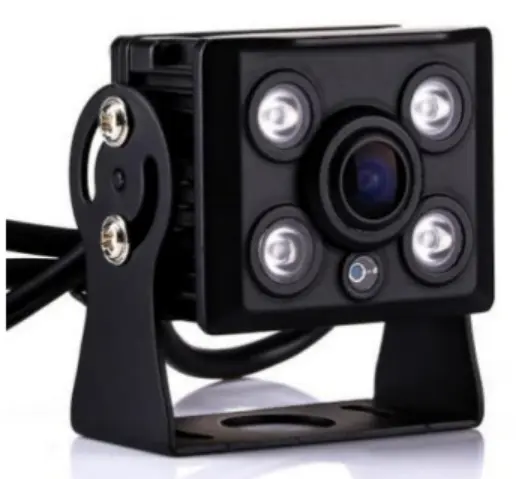
- High-definition square waterproof camera: Suitable for front or right-side blind spot monitoring.

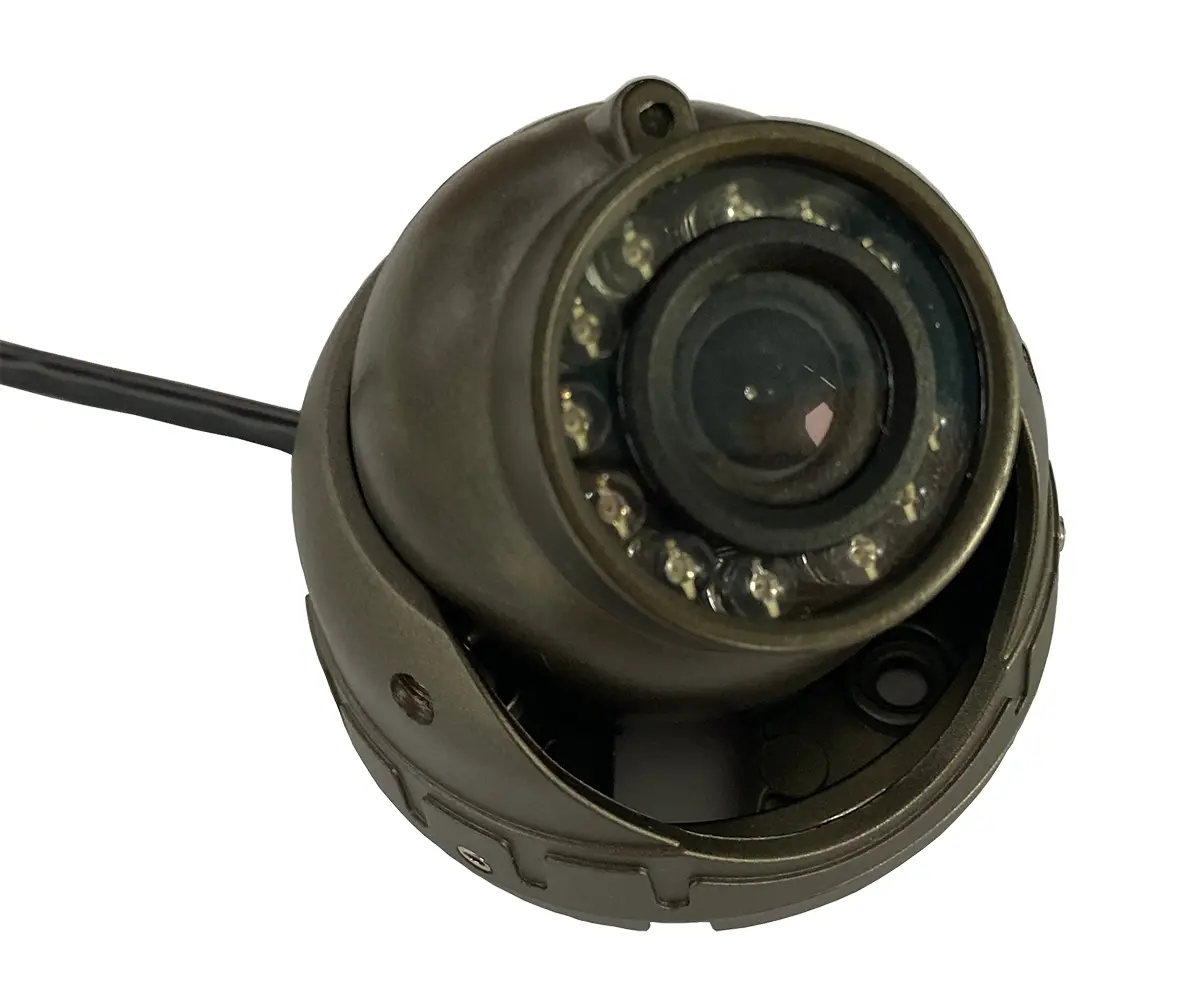
- High-definition cassette-mounted waterproof camera: Suitable for side blind spots, particularly the right side.
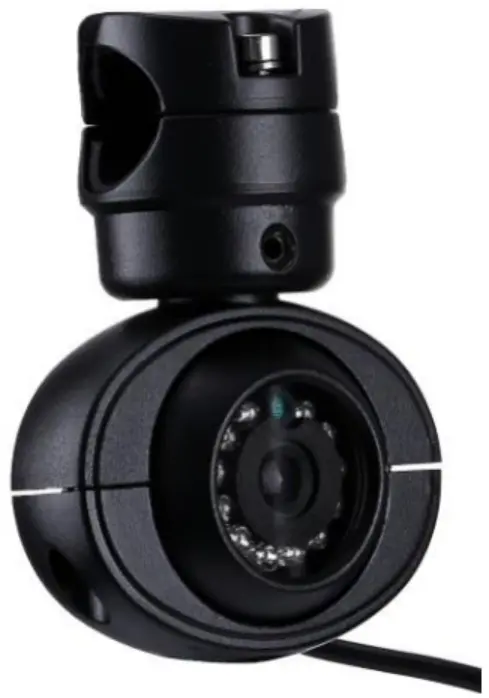

- High-definition mouse-shaped waterproof camera: Suitable for side blind spots, mounted on the side of the vehicle.

- High-definition large square waterproof camera (reversing camera): Used for rear blind spot monitoring.

Considerations When Using the Blind Spot Detection (BSD) System
1. Understand the System's Range: Every BSD system has a specific detection area, so it's essential to understand the actual monitoring range.
2. Don’t Rely Solely on the System: The BSD system is an auxiliary tool, and drivers should still remain alert by using traditional methods (like mirrors and shoulder checks).
3. Weather and Environmental Limitations: Weather conditions such as heavy rain, snow, or fog, or dirt on sensors, can affect the system's accuracy.
4. Sensor Maintenance: Regularly clean sensors to ensure they work properly.
The Value of Blind Spot Detection Systems
Investing in a Blind Spot Detection (BSD) system is worthwhile, especially for those who frequently drive in dense traffic, on highways, or with vehicles that have significant blind spots, such as SUVs and trucks. Research has shown that BSD systems can reduce the occurrence of lane-change accidents and the injuries resulting from them.
Main Applications:
- Lane Change Assistance: Detects vehicles in adjacent lanes that are outside the driver’s line of sight, reducing the risk of side collisions.
- Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA): Helps drivers detect vehicles coming from the side when parking or reversing.
- Highway Driving Assistance: Monitors blind spots while driving at high speeds, aiding in safe lane changes.
- Pedestrian and Cyclist Detection: Identifies vulnerable road users in urban environments and issues alerts.
Blind Spot Detection (BSD) systems significantly enhance driving safety by reducing accidents and injuries. An increasing number of vehicle owners are retrofitting their cars with BSD systems due to the lack of this technology in older models. As a leading provider of vehicle safety solutions, YUWEI is committed to offering top-tier BSD systems to enhance your driving safety. If you are interested in equipping your vehicle with a BSD system, please feel free to contact us!